Links to Compromised Websites
Scams
September 19, 2024
The NJCCIC’s email security solution detected multiple phishing campaigns attempting to deliver messages containing links to websites compromised by a payment skimmer. Digital skimmers are snippets of code injected into online retailers that steal payment details as they are entered. The compromised websites contain an injection with a single line of code in the footer, specifically, a simple script tag that loads content from a remote website. The response from the injection includes a function to retrieve information from the site from which it is being called. The compromised website’s domain name is passed into another URL to retrieve the obfuscated JavaScript skimmer code.

During checkout, a fake “Payment Method” frame is inserted within the retailer’s webpage. If the user enters payment details into the page, the data is transmitted in real time and stored in the threat actor’s database. Analysts detected the campaign targeting online retailers using the Magento e-commerce platform, identifying dozens of attacker-controlled websites and hundreds of compromised online retailers. These attacks cannot be detected by popular web
security methods, such as web application firewalls (WAFs), and are executed on the client side, prolonging the attack and potentially resulting in tens of thousands of victims and damage to the reputations of victimized organizations. Additionally, consumers’ PII and credit card information are at risk of being stolen or sold on dark web forums.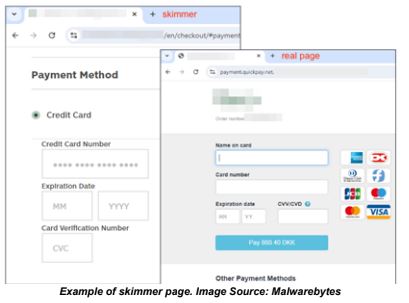
Recommendations
- Online retail customers can minimize their risk of data exposure by using electronic payment methods or virtual cards and setting charge limits.
- Consider using credit cards over debit cards when shopping online, as they often have better consumer fraud protections.
- Enable payment charge notifications for a set transactional amount with the financial institution, which may allow customers to identify fraudulent transactions promptly.
- If fraudulent activity is discovered, notify the banking institution immediately and request a new payment card.
- Website administrators are encouraged to block access to sensitive information entered in web forms and stored cookies.
- Consider leveraging tools and technologies that provide behavioral and anomaly detection of in-browser activity.
- Keep systems up to date and apply patches after appropriate testing.
- Use strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all accounts where available, choosing authentication apps or hardware tokens over SMS text-based codes.
- Indicators of compromise (IOCs) and technical details can be found in the Malwarebytes blog post.