PRC State-Sponsored APT40 Tactics
Global Attacks
July 11, 2024
A joint international cybersecurity advisory from agencies and law enforcement across eight countries, including the US, warns of the recently observed tactics used by the Chinese state-sponsored APT40, also known as Kryptonite Panda, GINGHAM TYPHOON, Leviathan, and Bronze Mohawk. This group conducts malicious cyber operations for the People’s Republic of China (PRC) Ministry of State Security (MSS). APT40 is known to conduct malicious cyber operations on behalf of the PRC’s Ministry of State Security Department (MSS) and is based in Haikou, Hainan Province, PRC.
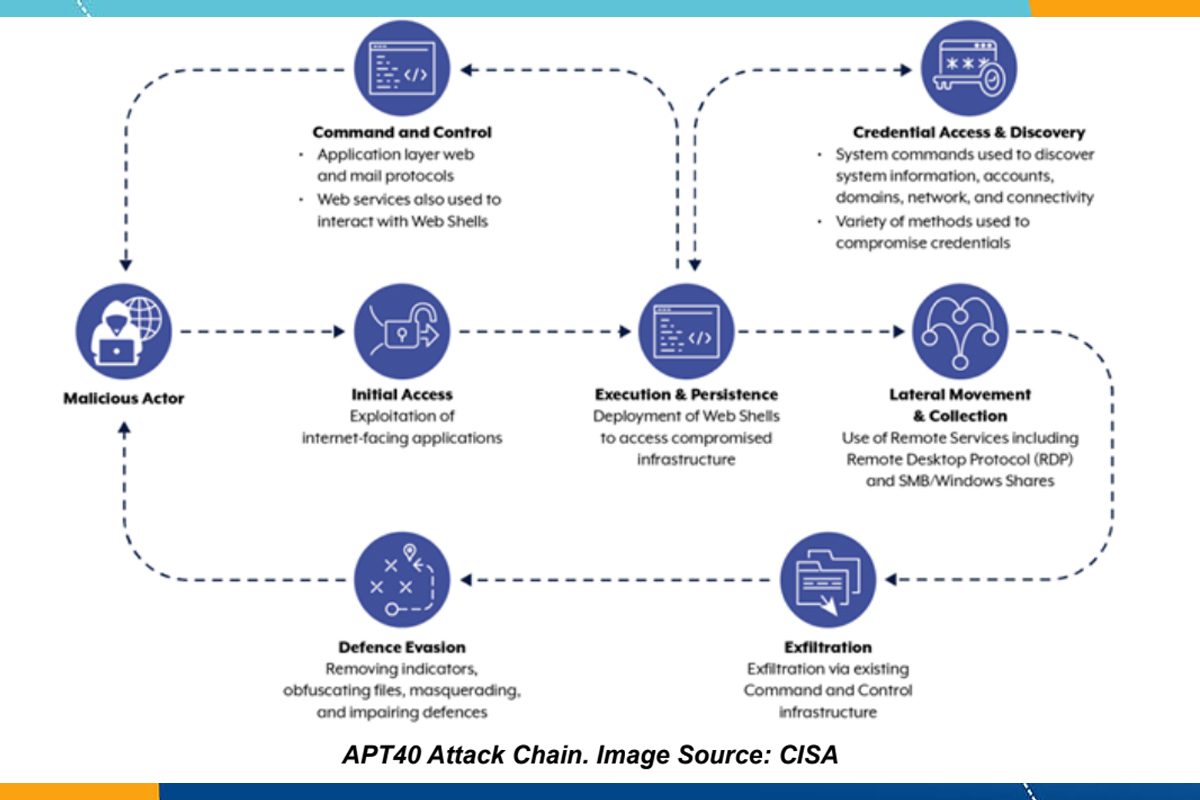
APT40 regularly conducts reconnaissance against networks in the authoring agencies’ countries. The group typically identifies vulnerable, end-of-life (EOL), or unmaintained devices on networks of interest and rapidly deploys exploits leveraging old and new vulnerabilities. The threat group is known to quickly adapt and develop exploits for new vulnerabilities, including those in widely used software such as Atlassian Confluence (CVE-2021-26084), Log4J ( CVE-2021-44228), and Microsoft Exchange (CVE-2021-31207, CVE-2021-34523, CVE-2021-34473). Analysts anticipate that the threat group will continue to promptly employ proof of concepts (PoCs) to address newly identified high-profile vulnerabilities within hours or days of public disclosure.
The hacking group was recently observed compromising legacy small-office/home-office (SOHO) devices and using them as launching points for subsequent attacks, allowing the malicious activities to disguise themselves within legitimate network traffic. While accessing the compromised devices, the group collected credentials, multi-factor authentication (MFA) token values, and JSON Web Tokens (JWTs), an authentication artifact used to create virtual desktop login sessions. The threat actor may have been able to use these to create or hijack virtual desktop sessions and access the internal organization network segment as a legitimate user. They also exploited access to the compromised device to extract data from an SQL server located within the organization’s internal network. In the final phase, APT40 accessed SMB shares and exfiltrated data to a command and control (C2) server while removing event logs and deploying software to maintain a stealthy presence on the breached network.
Network segmentation limits lateral movement by denying traffic between computers unless required and can make it significantly more difficult for adversaries to locate and gain access to an organization’s sensitive data. Regardless of instances identified where lateral movement is prevented, additional network segmentation may limit the data the threat actors can access and extract. Most exploited vulnerabilities were publicly known, and patches or mitigations were available.
Recommendations
- Keep systems up to date and apply patches after appropriate testing.
- Utilize monitoring and detection solutions to identify suspicious login attempts and user behavior.
- Enforce the principle of least privilege, disable unused ports and services, and use web application firewalls (WAFs).
- Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) where available, choosing authentication apps or hardware tokens over SMS text-based codes.
- Employ a comprehensive data backup plan and ensure operational technology (OT) environments are segmented from information technology (IT) environments.
- Report ransomware and other malicious cyber activity to the FBI’s IC3 and the NJCCIC.