WarmCookie Campaigns Resurface
Malware
October 31, 2024
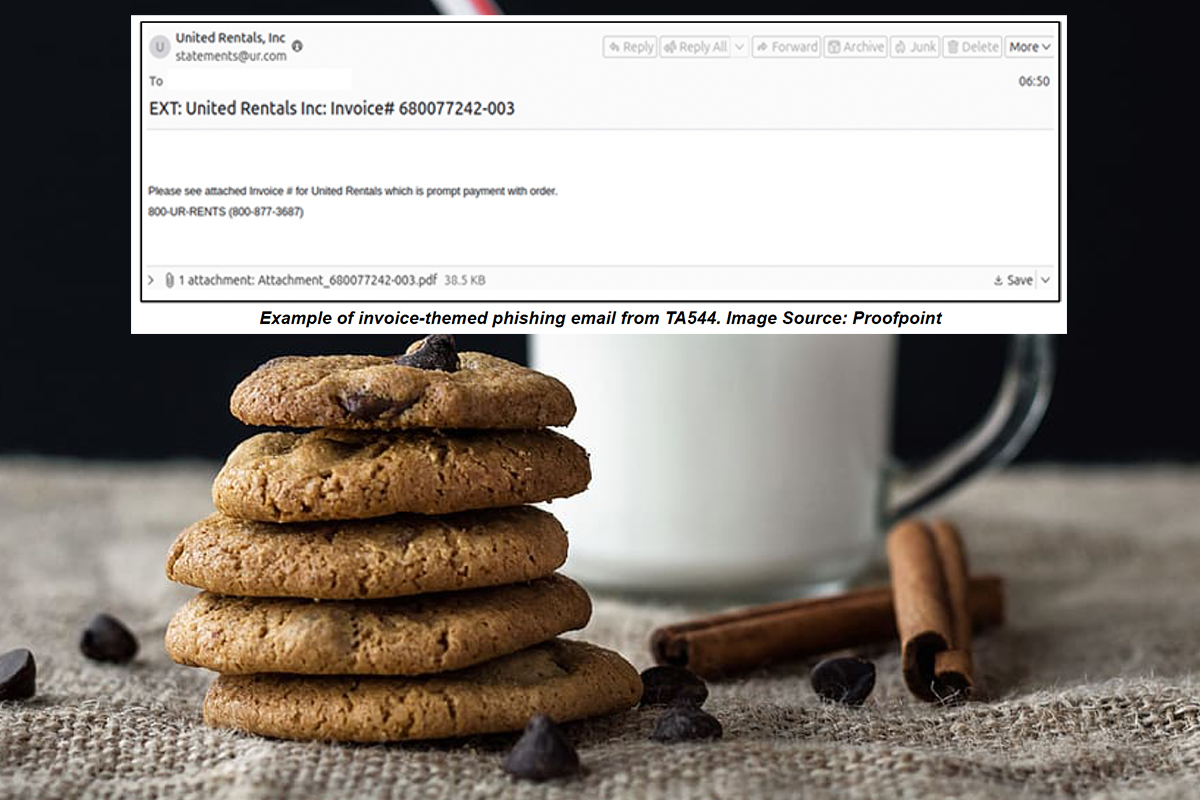
The NJCCIC’s email security solution detected a campaign linked to TA544, also referred to as Bamboo Spider and Zeus Panda, which has recently reemerged after a period of inactivity since their campaign in August. Similar to open-source reporting , this new campaign attempts to distribute the WarmCookie backdoor, using invoice lures in phishing emails that impersonate legitimate businesses like United Rentals, Inc. The email messages typically include a PDF attachment that contains embedded URLs. If these URLs are clicked, the recipient is directed to download a zipped JavaScript file. If executed, the file uses a PowerShell script and bitsadmin to install a dynamic link library (DLL) and deploy WarmCookie. This method of operation closely mirrors TA544’s previous tactics observed in the August campaign. The associated command and control (C2) server IP used in this campaign is 185[.]161[.]251[.]26, and PDF URLs include the root domain, servermacosdomain[.]com.

WarmCookie, or BadSpace, is a two-stage Microsoft Windows backdoor primarily distributed via phishing. It features command handlers for gathering victim information, harvesting credentials, recording screenshots, and launching additional payloads. The backdoor is easy to use, enabling less experienced threat actors to deploy more destructive payloads like ransomware.
Additionally, analysts attributed recently observed WarmCookie activity to TA866, also known as Asylum Ambuscade. This campaign appears to rely on malspam or malvertising to initiate the infection process. In the malspam examples, themes include invoices and employment agency-related topics. In an early campaign, analysts observed the use of the LandUpdates808 cluster of infrastructure. They noted that malicious JavaScript downloaders were hosted on servers associated with the LandUpdates808 web server cluster.
Recommendations
- Avoid clicking links, responding to, or otherwise acting on unsolicited emails.
- Confirm requests from senders via contact information obtained from verified and official sources.
- Keep systems up to date and apply patches after appropriate testing.
- Implement cybersecurity best practices to reduce risk and increase resiliency to cyber threats.
- Utilize monitoring and detection solutions to identify suspicious login attempts and user behavior.
- Conduct continuous monitoring and threat hunting. Ingest indicators of compromise (IOCs) and techniques found in the Cisco Talos blog post and the Hunt Intelligence blog post into endpoint security solutions.
- Consider leveraging behavior-based detection tools rather than signature-based tools.
- Implement controls around Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) Jobs by modifying network or host firewall rules and other network controls to allow only legitimate BITS traffic.
- Phishing and other malicious cyber activity can be reported to the FBI’s IC3 and the NJCCIC.